Introduction to CrypticNeo
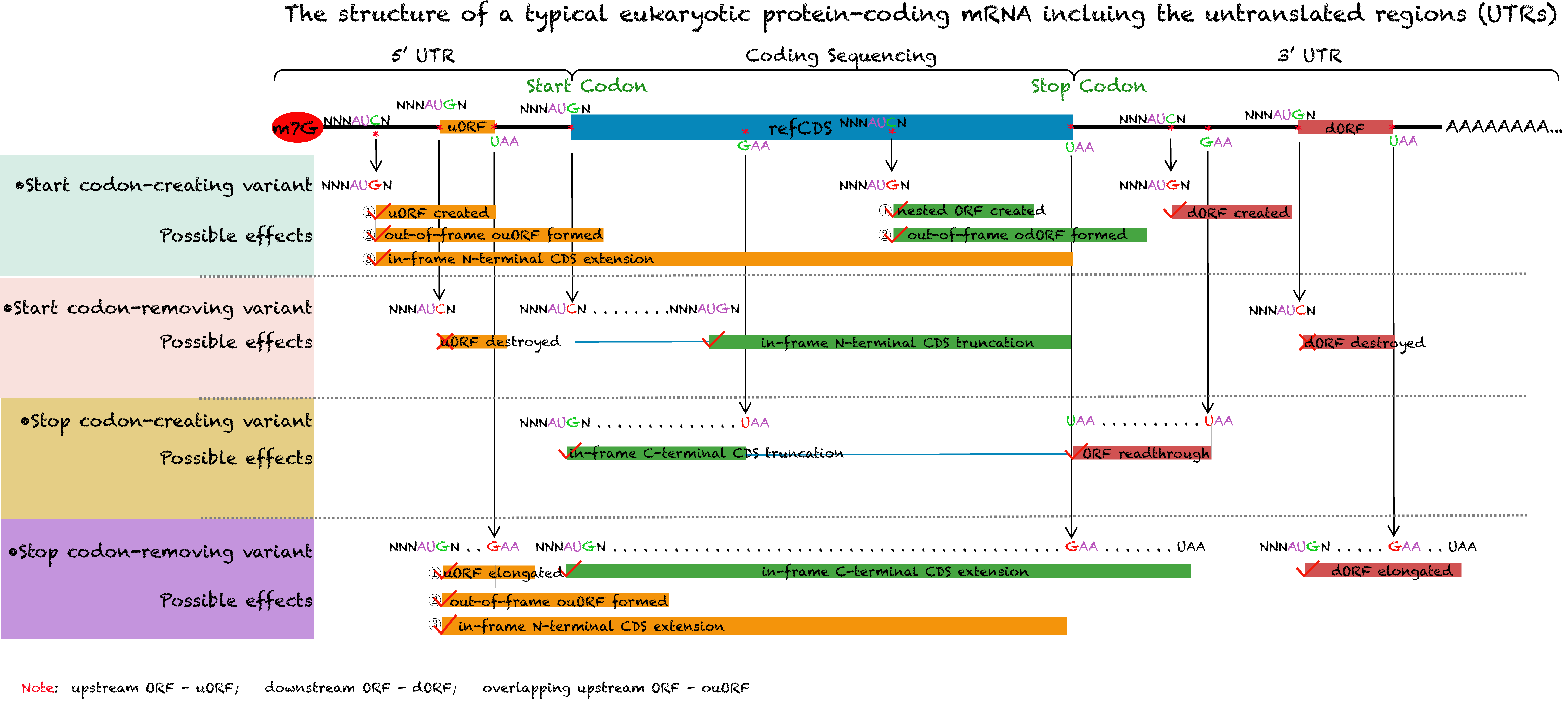
A growing body of evidence utilizing high-throughput ribosome profiling (ribo-seq) has shown pervasive translation of non-canonical human open reading frames (ORFs), of which some encoded protein products have been demonstrated to have major implications for human health and disease. Nevertheless, less is known about the effects of genetic variants that create or disrupt non-canonical translated ORFs and potential contribution of this class of variation to human genetic disease. Here, we developed a novel database named ORFVar, which aims at provide a comprehensive resource of functional genetic variants associated with non-canonical human open reading frames.
In the current version, ORFVar contains 302,404 unique actively translated ORFs, including upstream ORFs (uORFs), downstream ORFs (dORFs), novel ORFs in non-coding RNAs, extended and truncated ORFs, and 4,135,579 genetic variations with different effects on ORF translation, including as start/stop-creating and/or removing variations as well as protein-coding missense variants.
News
15/6/2025
CrypticNeo is freely accessible.
5/1/2025
CrypticNeo is created.
Citation
Please cite our work when using this resource in your publications:
"CrypticNeo: A Compendium of cryptic neoantigens translated from noncanonical ORFs".